What is a Point-of-Sale?
The Point-of-Sale (POS) in a store is the place that you pay for your purchases. It is usually where the till (cash register) is located.
A typical POS will have...
A typical POS will have...
- A method of inputting the codes of goods purchased - usually a bar-code scanner. The codes are then used to find more information about the goods, such as price, from a database
- A system to accept electronic payments - EFTPOS (see below)
- A system to update the stock-level of goods whenever they are sold, and possibly to automatically re-order goods that have low stock-levels (see below)
- A method of producing a receipt for purchases - usually a small dot-matrix printer


Handling Electronic Payments (EFTPOS)
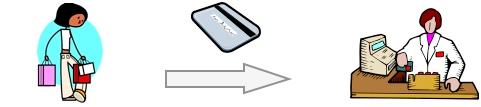
When you use a bank card to pay for a purchase in a store, the payment is made using a system called Electronic Fund Transfer at Point-of-Sale (EFTPOS).
This is how it works…
This is how it works…
The EFT in EFTPOS is the same Electronic Fund Transfer system discussed here.
1
Customer gives the bank card to the cashier
2
The cashier runs the card through a card reader (the customer may have to enter a PIN). The cashier enters the value of the purchase

3
The store’s system then connects to the bank computer and sends a message

4
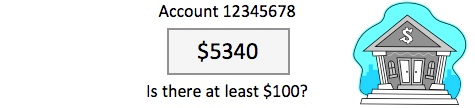
The bank computer uses the account number to access the customer’s record and checks the balance
5
The bank computer sends back a confirmation or rejection message to the store’s system

6
The cashier now confirms the purchase and an EFT message is sent to the bank

7
The bank computer subtracts $100 from the customer’s account and adds $100 to the store’s account
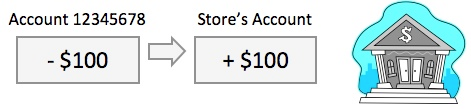
8
The cashier gives the card back to the customer along with a receipt
'Chip & PIN' Payment System
Most bankcards no longer rely on a magnetic strip to store customer account details. Instead the cards are smart cards. The cards contain a small amount of computer memory with the account information stored inside.
Smart cards are more secure (since the data is encrypted) and more reliable than magnetic strip cards.
When a customer wishes to pay for goods in a store, the customer inserts the bankcard into a smart card reader, and then types in a PIN to confirm that they are the true owner of the card. Once the PIN is verified, the customer can remove the card.
One of the reasons this system has proven popular is the extra level of security it provides for users: At no time does the bankcard need to be handled by anyone other than the card owner, so with this system there is less chance of the card being stolen or copied.
The nickname for the tiny memory device inside the bankcard is a ‘chip’, and the system uses a PIN as identity proof, so the system is nicknamed ‘Chip and PIN’ in the UK.
Smart cards are more secure (since the data is encrypted) and more reliable than magnetic strip cards.
When a customer wishes to pay for goods in a store, the customer inserts the bankcard into a smart card reader, and then types in a PIN to confirm that they are the true owner of the card. Once the PIN is verified, the customer can remove the card.
One of the reasons this system has proven popular is the extra level of security it provides for users: At no time does the bankcard need to be handled by anyone other than the card owner, so with this system there is less chance of the card being stolen or copied.
The nickname for the tiny memory device inside the bankcard is a ‘chip’, and the system uses a PIN as identity proof, so the system is nicknamed ‘Chip and PIN’ in the UK.

PIN stands for Personal Identification Number.
A PIN is usually a four digit secret code used to confirm a person’s identity (e.g. when withdrawing cash from an ATM)
Note: You should not say ‘PIN number’ since that would mean ‘Personal ID Number number’!
A PIN is usually a four digit secret code used to confirm a person’s identity (e.g. when withdrawing cash from an ATM)
Note: You should not say ‘PIN number’ since that would mean ‘Personal ID Number number’!
Automatic Re-Ordering of Stock
In many stores, the POS system is linked to the stock control system...
'Stock' means the things that you have in your store / warehouse.
'Stock Control' is the system that keeps track of what you have in stock
'Stock Control' is the system that keeps track of what you have in stock
1
When goods are sold, the POS system send the details of the sale to the stock-control system
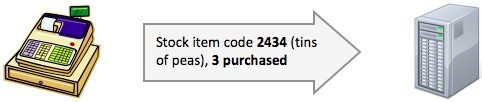
2
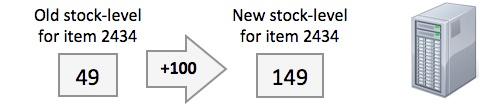
The stock-control system updates the stock-levels in the stock database for the purchased goods
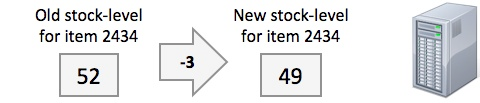
3
If the stock-level falls below a pre-set value, the stock-control system sends an order to the suppliers

4
The suppliers send a delivery to the store.
5
The stock-control system updates the stock-levels in the stock database for the delivered goods
Internet Shopping (e-Commerce)
In the last few years, Internet shopping has become very popular. Stores like Amazon and the iTunes Store are some of the largest retail businesses in the world. Online you can buy anything from air flights to fresh eggs.
Customers like Internet shopping because...
Customers like Internet shopping because...
- The convenience of being able to browse goods from your home
- Stores are open 24 hours a day, every day of the year
- The wider range of choice - can access stores all over the world
- Easy if you have limited mobility (due to a disability, or old age)
- Goods are often cheaper than in stores
- Payment is simple using credit cards or services such as PayPal
- Lower costs since no expensive retail stores and less staff
- Lower costs = lower selling prices = higher sales = bigger profits
- Many more potential customers
- You cannot try items before purchasing (e.g. clothes)
- You may have to wait several days before receiving your goods
- Returning goods or getting help can be difficult
- There is a security risk using credit cards online. The card details may be stolen and used to commit fraud.