Good communication is essential to every organisation: communication between organisations, and communication between parts of a single organisation (e.g. between offices in different countries).
A wide variety of communication systems are used...
A wide variety of communication systems are used...
Before the Internet, most business communication was via telephone, fax, telex (a way of sending text messages that printed out on a printer), or by using mail - the old-fashioned paper version!
E-mail is a system that allows messages to be sent and received by computers. E-mail is the most common form of electronic communication.
E-mail messages are text-based, but other types of file can also be sent as ‘attachments’.
E-mails that are received wait in a user's inbox until the user is ready to read them. (Unlike a telephone call, the user is free to ignore e-mails until they have time to deal with them.)
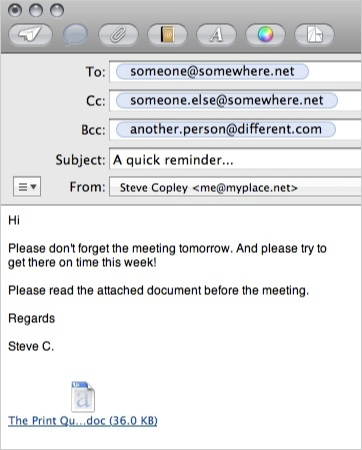
An e-mail message usually has the following parts:
E-mail messages are text-based, but other types of file can also be sent as ‘attachments’.
E-mails that are received wait in a user's inbox until the user is ready to read them. (Unlike a telephone call, the user is free to ignore e-mails until they have time to deal with them.)
An e-mail message usually has the following parts:
To send and receive e-mail, you need to have an e-mail address.
An address is made up of two parts: a username and an e-mail provider, with an '@' symbol in the middle:
An address is made up of two parts: a username and an e-mail provider, with an '@' symbol in the middle:
username@provider
| To | The address(es) of the person who the message is for |
| Subject | A short sentance describing what the message is about |
| Message | The text of the message. This can be as long as you like |
An e-mail may also include the following parts:
| CC | The address(es) of people to copy the e-mail to (Carbon Copy) |
| BCC | The address(es) of people to copy the e-mail to without anyone else knowing (Blind Carbon Copy) |
| Attachments | Files linked to the message (images, documents, etc.) |

Video Conferencing
Video-conferencing is a system that allows people to have conversations and meetings with other people in different locations, but without leaving their office.
A video-conference involves people sitting in front of a camera and a microphone, whilst watching other people of a screen and listening to them through loudspeakers.
Note: The camera is usually TV quality - much better than a standard webcam.
A video-conference involves people sitting in front of a camera and a microphone, whilst watching other people of a screen and listening to them through loudspeakers.
Note: The camera is usually TV quality - much better than a standard webcam.

The system uses the following hardware:
- Video camera
- Monitor
- Microphone
- Loudspeakers
- High-speed network / Internet connection
- No travel costs
- No time wasted travelling to other cities / countries
- Can organise meetings at short notice
- Less personal than face-to-face meetings
- Documents (e.g. contracts) cannot be signed

Mobile Telephones
Mobile telephones allow people to be away from their workplace, yet still be contactable. This means that people can still work, even when out of the office.
Modern smart-phones can perform a wide variety of tasks:
Modern smart-phones can perform a wide variety of tasks:
- Make and receive telephone calls just about anywhere
- Send a receive SMS (short message service) messages
- Send and receive e-mail
- Send and receive files such as images, text documents, etc.
- Edit documents
- Most people would be lost without their mobile phone!
- Workers never get a chance to 'switch off' since they can always be contacted - can be stressful
- Mobiles are easy to lose, and often contain a lot of personal and/or business information. A lost mobile could be embarrassing / damaging if the wrong people got hold of it

Internet Telephony / Voice Over IP (VOIP)
Internet telephony, or 'VOIP', is becoming very popular both for personal use, and within the workplace.
Instead of using the normal telephone network (designed to carry voices using analogue signals), VOIP systems send voices through the Internet as digital data, just like any other Internet data (e.g. e-mails, files, webpages, etc.)
In other words, VOIP systems use your Internet connection to send and receive phone calls.
Instead of using the normal telephone network (designed to carry voices using analogue signals), VOIP systems send voices through the Internet as digital data, just like any other Internet data (e.g. e-mails, files, webpages, etc.)
In other words, VOIP systems use your Internet connection to send and receive phone calls.
'Internet Telephony' means a telephone system that uses the Internet
'VOIP' means Voice Over IP, where IP means Internet Protocol - the system that the Internet uses to transfer all data
'VOIP' means Voice Over IP, where IP means Internet Protocol - the system that the Internet uses to transfer all data
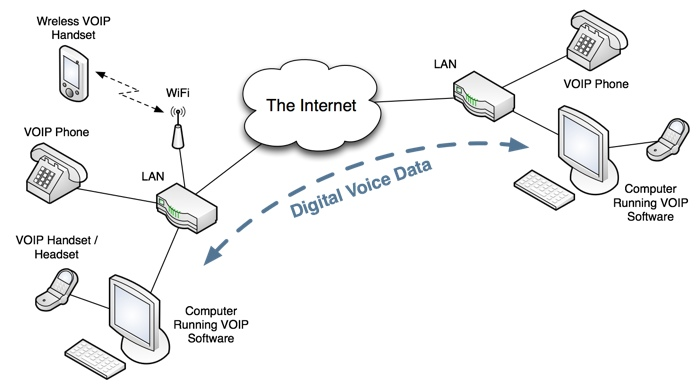
VOIP systems can work in several ways:
- VOIP software can be installed on a computer. Calls are then made using a headset (headphones / microphone) or by using a special USB handset (looks just like a normal phone)
- Special VOIP telephones can be plugged directly into the network (or can connect wirelessly using WiFi)
- No telephone line is required
- Call costs are very low, especially for long-distance calls
- Can include video
- Require special hardware and an Internet connection
- Not as reliable as normal phones, so cannot be relied upon for emergency calls (911, or 999)
- Call quality depends on the speed of the Internet connection
The most well-known public VOIP service is Skype, but there are others such as Google Talk, Vbuzzer, Fring, ooVoo, and SightSpeed.
(Needless to say, the traditional phone companies don't like VOIP as it takes away their business!)
(Needless to say, the traditional phone companies don't like VOIP as it takes away their business!)



Fax
Fax is short for ‘facsimile’ which means ‘copy’.
A fax machine is a device that can send a copy of a paper document over the telephone network.
One reason that faxes are still used is that most businesses would accept a document such as a contract that had been signed, and sent by fax. (Electronically signing e-mail attachments is not yet widespread.)
A fax machine is a device that can send a copy of a paper document over the telephone network.
- The sending fax converts the light/dark areas of the printed document into noises.
- These noises travel through the phone system and are received by another fax machine.
- The receiving fax machine converts the noises into printed marks on a piece of paper - making a copy of the original document.
- Low quality - images are especially poor
- Slow to send (compared to e-mail)
One reason that faxes are still used is that most businesses would accept a document such as a contract that had been signed, and sent by fax. (Electronically signing e-mail attachments is not yet widespread.)


